Trabalho Prático 2
Introdução
Nesse segundo trabalho, o foco principal foi na utilização de sensores. Adquirimos conhecimentos que nos permitissem a construção, avaliação e processamento dos sinais medidos fornecidos pelos sensores. Tais sinais foram utilizados em algumas tarefas realizadas pelo robô.
O robô anteriormente construído foi adaptado para poder realizar diversas novas tarefas: seguir uma linha reta, preta, no chão; encontrar e ir em direção de uma fonte de luz polarizada pré-determinada; detectar a presença de blocos num caminho e, através da percepção de suas cores, empurrar, desviar-se para a esquerda e ou para a direita. A utilização de sensores para realizar tais requisitos se mostrou uma tarefa especialmente complicadas exigindo tratamento para imprecisão dos mesmos.
Sensores
Shaft Encoder
Os Shaft Encoders, que são capazes de medir a quantidade de rotações feitas por uma determinada peça circular. No caso, eles foram utilizados para a medição das rotações das rodas do robô para que, através de operações sobre este número, fosse estimada a distância que o robô se deslocou. Este método gera uma imprecisão considerável, uma vez que a as mais sutís imprecisões da superfície de contato sob o robô geravam erros nas mudanças, uma vez que nem sempre uma rotação da roda significava uma determinada distância percorrida.
Para aperfeiçoar o controle dos motores substituimos a biblioteca padrão do IC que controla os motores por uma biblioteca cutomizada por Julian Skidmore para obter maior resolução na gradação de potência do motor. Com a biblioteca padrão é possível variar a potência do motor em apenas 8 estágios, enquanto na biblioteca poroposta é possível varia a potência do motor em 100 estágios. A biblioteca encontra-se disponível em http://handyboard.com/oldhb/software/contrib.html na seção “Smooth PWM Routines”.
Sensor Diferencial
 Para cumprirmos a tarefa de ir em direção a uma luz polarizada utilizamos a montagem de um sensor diferencial de luminosidade. A luz polarizada nada mais é do que uma fonte de luz que é coberta com um filtro polarizador. Com isso, a luz passa somente em uma direção específica (no nosso caso as direções foram horizontal e vertical). O sensor diferencial de luminosidade foi montado utilizando dois LDRs (do inglês light dependent resistor). Cada LDR foi coberto com o filtro nas direções utilizadas. Na prática, utilizando apenas uma entrada analógica conseguimos detectar e diferenciar ambas as fontes de luz polarizada. Pela montagem realizada, ao voltarmos os sensores para a luz vertical temos uma leitura de uma resistência baixa e para a luz horizontalmente polarizada temos uma leitura indicando uma resistência alta.
Para cumprirmos a tarefa de ir em direção a uma luz polarizada utilizamos a montagem de um sensor diferencial de luminosidade. A luz polarizada nada mais é do que uma fonte de luz que é coberta com um filtro polarizador. Com isso, a luz passa somente em uma direção específica (no nosso caso as direções foram horizontal e vertical). O sensor diferencial de luminosidade foi montado utilizando dois LDRs (do inglês light dependent resistor). Cada LDR foi coberto com o filtro nas direções utilizadas. Na prática, utilizando apenas uma entrada analógica conseguimos detectar e diferenciar ambas as fontes de luz polarizada. Pela montagem realizada, ao voltarmos os sensores para a luz vertical temos uma leitura de uma resistência baixa e para a luz horizontalmente polarizada temos uma leitura indicando uma resistência alta.
Sensor Opto-reflexivo
 Esse sensor consiste de um emissor e de um receptor infra-vermelho encapsulados em um invólucro plástico e posicionados em um alinhamento ideal para para tal apliação. O emissor emite um feixe de luz que é refletido pelo obejto e captado pelo receptor que gera um sinal elétrico em função da intensidade do feixe de luz recebido. Na prática, utilizamos uma porta digital fizemos uma montagem para que obtivessemos uma leitura verdadeira (1) numa superfície branca e falsa (0) numa preta. Esse sensor foi utilizado para a tarefa de seguir uma faixa preta no chão.
Esse sensor consiste de um emissor e de um receptor infra-vermelho encapsulados em um invólucro plástico e posicionados em um alinhamento ideal para para tal apliação. O emissor emite um feixe de luz que é refletido pelo obejto e captado pelo receptor que gera um sinal elétrico em função da intensidade do feixe de luz recebido. Na prática, utilizamos uma porta digital fizemos uma montagem para que obtivessemos uma leitura verdadeira (1) numa superfície branca e falsa (0) numa preta. Esse sensor foi utilizado para a tarefa de seguir uma faixa preta no chão.
Sensor Break-beam
Esse sensor foi construido com um LED azul e um LDR posicionados um de frente para o outro. Quando algum objeto se põe entre o LED e o LDR a luz não sensibiliza o LDR. Assim, utilizamos uma porta digital onde lê-se 0 quando um objeto é encontrado.
Sensor de Cor
 Esse sensor foi construido com um LED RGB e um LDR. Esse LED emite luz vermelha, verde e azul. Essas luzes são jogadas alternadamente sobre um objeto e a reflexão pode ser lida em uma entrada analógica com o LDR. Cada cor tem leituras diferentes de reflexão, medidas para comparação foram realizadas e são utilizadas como base para nominar a cor do objeto.
Esse sensor foi construido com um LED RGB e um LDR. Esse LED emite luz vermelha, verde e azul. Essas luzes são jogadas alternadamente sobre um objeto e a reflexão pode ser lida em uma entrada analógica com o LDR. Cada cor tem leituras diferentes de reflexão, medidas para comparação foram realizadas e são utilizadas como base para nominar a cor do objeto.
Abaixo estão alguns gráficos com valores das leituras da reflexão da luz nos blocos.

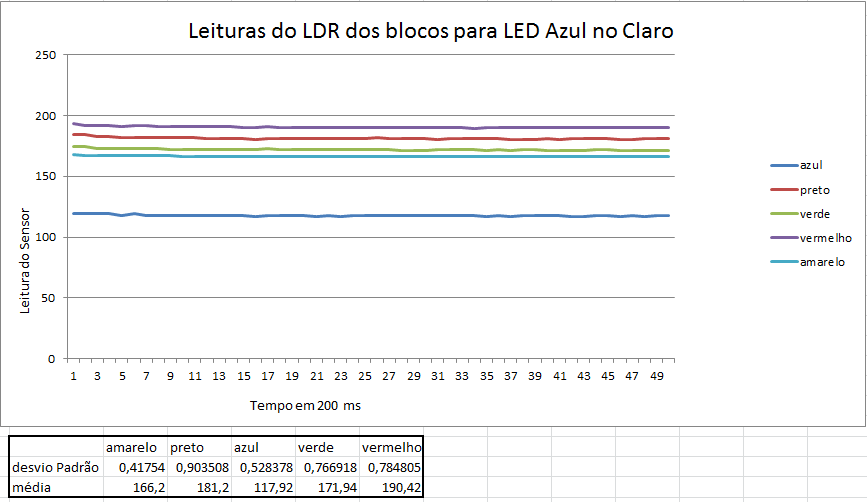



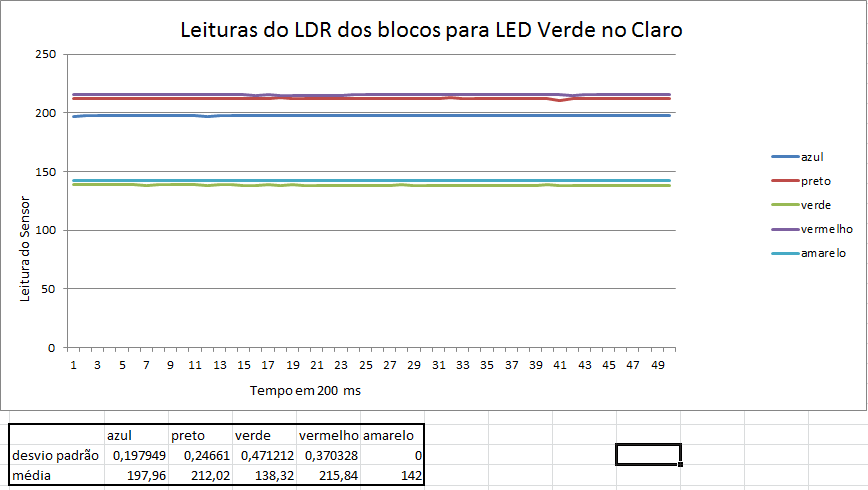

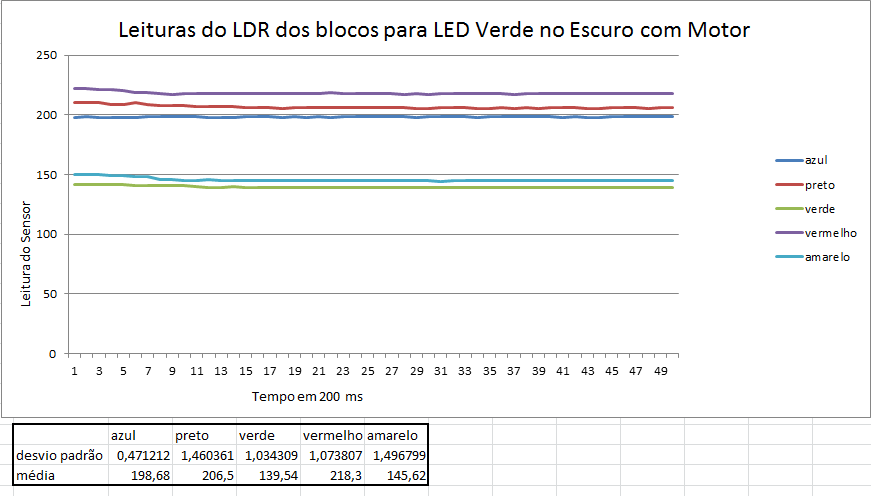
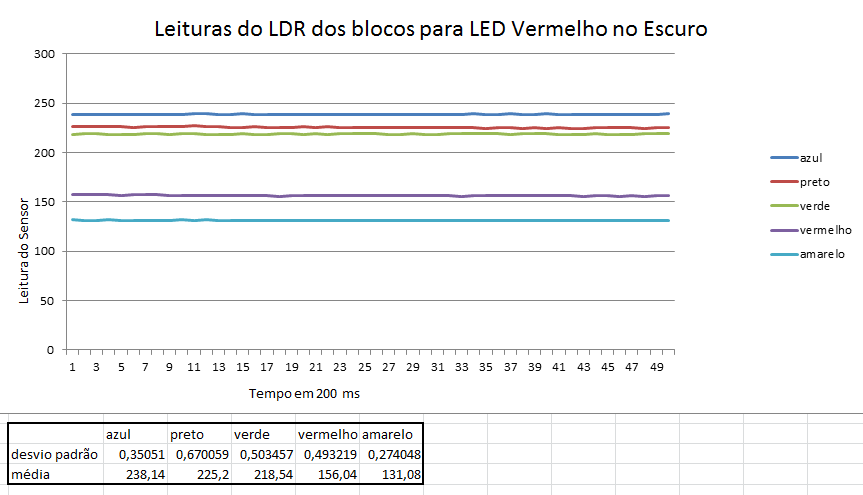
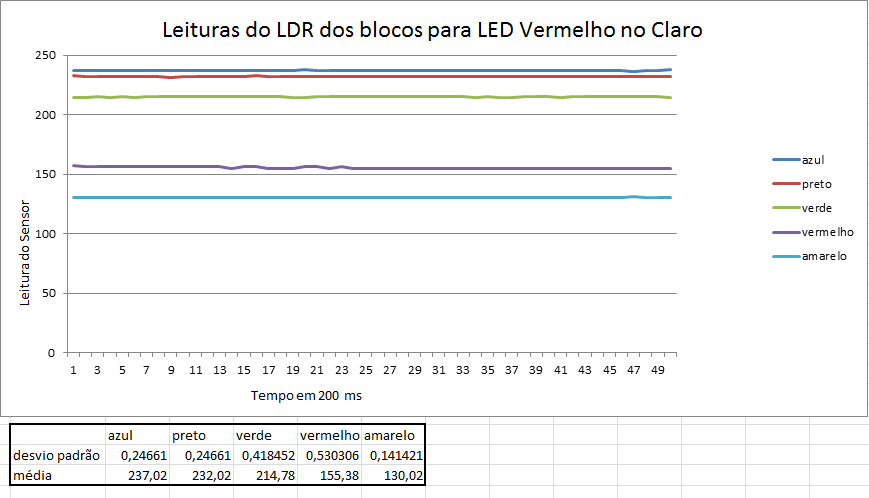

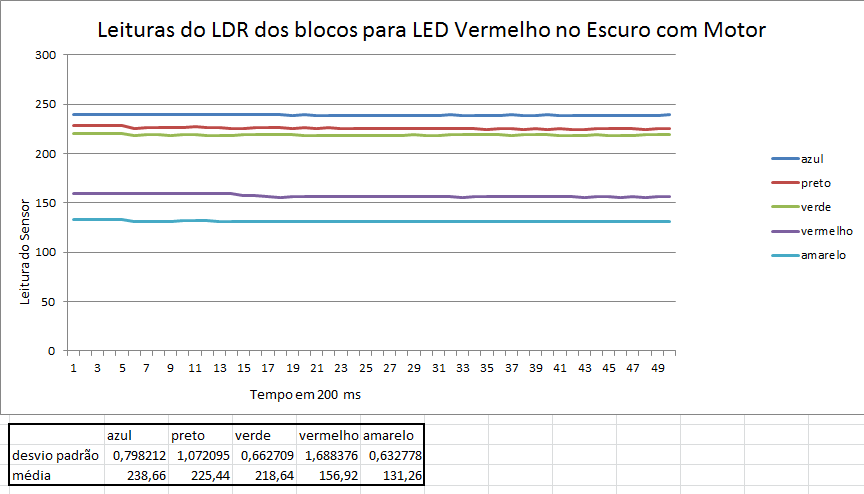
Como pode ser percebido anteriormente através dos gráficos, os menores erros ocorrem quando as leituras são feitas com os motores desligados e em um ambiente escuro.
Fizemos também testes com o bloco situados a 3 distâncias do sensor, e a que obteve melhores resultados foi a distância de 1 cm. Distâncias menores que 1cm, o sensor não consegue captar a luz refletida e maiores que 1 cm, a luz refletida se dissipa e as medições perdem muita precisão.
Tarefas Realizadas
Localização da Luz Polarizada
Essa tarefa foi realizada utilizando o sensor diferencial de luz polarizada e um sensor LDR simples. O sensor LDR simples foi utilizado para diminuir a interferência da luz ambiente. A solução encontrada foi a seguinte: o robô gira em torno do próprio eixo fazendo leituras com os sensores. Se a meta for a luz polarizada verticalmente o sensor diferencial fará uma leitura que tenderá para 0, e o sensor normal, como estará apontado para uma fonte de luz terá uma leitura que tenderá para 0 também, neste caso o robô gira 360 graus e armazena o menor valor de (leitura_sensor_diferencial+leitura_sensor_normal), o robô então gira novamente em torno de seu eixo e procura por este menor valor que indica aonde a luz polarizada está e então segue nesta direção. Se a meta for a luz horizontalmente polarizada, o sensor diferencial fará uma leitura que tenderá para 255, e o sensor normal, como estará apontado para uma fonte de luz terá uma leitura que tenderá para 0, neste caso o robô gira 360 graus e armazena o maior valor de (1000+leitura_sensor_diferencial-leitura_sensor_normal), o robô então gira novamente em torno de seu eixo e procura por este maior valor que indica aonde a luz polarizada está e então segue nesta direção. Vale lembrar que o acrescentamos 1000 na formula anterior somente para que o valor não fique negativo.
Seguir Linha
Essa tarefa consistia em localizar uma linha preta traçada no chão com fita isolante e, utilizando os devidos sensores, seguir o trajeto traçado pela mesma, corrigindo os devidos erros de sensoreamento. Utilizamos para tal dois sensores opto-reflexivos, descritos acima, que corrigiam o trajeto do robô quando este saia do trajeto preto. Numa situação de deslocamento ideal, ambos os sensores detectavam superfícies pretas sob si
Identificação da Cor dos Blocos
Nesta tarefa utilizamos os sensores de cor, um montado na frente do robô e dois montados em suportes à frente do mesmo, de modo a cercar qualquer bloco encontrado por três sensores em lados diferentes. Através das leituras, refinadas exaustivamente através de constantes medições e testes, a cor bloco era identificada e o robô reagia de acordo: hora empurrando o bloco, hora parando de se deslocar, hora se desviando do bloco pela direita ou pela esquerda. O trajeto seguido pelo robô para encontrar e interagir com os blocos era indicado pela fita preta.
Ao detectar o bloco, utilizando o sensor break-beam, passamos a detecção de cor com o sensor construido para tanto. O LED RGB emite a luz vermelha, depois verde e por fim azul e o ldr faz leituras da reflexão da luz emitida para cada cor, e de acordo com as leituras, determina a cor do bloco. Após determinada a cor do bloco, uma ação que foi determinada anteriormente é então executada.
Vídeo da apresentação final
Software do Projeto
#include sencdr0.icb #include sencdr4.icb #define SENS_OPT_L 7 #define SENS_OPT_R 8 #define SENS_OPT_B 10 #define SENS_DIF 6 #define SENS_CDR 5 #define SENS_COL 2 #define MOTOR_R 3 #define MOTOR_L 1 #define SENS_BRE 14 #define SENS_COLOR 6 #define RED 0 #define GREEN 1 #define BLUE 2 #define YELLOW 3 #define BLACK 4 #define LED_R 0b00100000 #define LED_G 0b00000100 #define LED_B 0b00001000 #define LED_SENS 0b00010000 #use "cmucamlib.ic" char buff[11]; int vermelho, verde, azul, amarelo, preto,tempoEmp; char menu_principal[2][30]={"Menu: Seguir Luz","Menu: Seguir Linha"}; char menu_seguir_luz[2][30]={"Menu: Vertical","Menu: Horizontal"}; char menu_seguir_linha[6][30]={"Vermelho", "Verde", "Azul", "Amarelo", "Preto", "Done"}; char menu_acao_cor[4][30] = {"Direita", "Esquerda", "Empurrar", "Parar"}; int push_red, push_green, push_blue, push_yellow, push_black; void main(){ int sel, config; vermelho = 3; verde = 2; azul = 0; amarelo = 1; preto = 3; push_red = 2; push_green = 2; push_blue = 2; push_yellow = 2; push_black = 2; printf("Parallel Mind - Press START\n"); while(!start_button()); msleep(100L); poke(0x1009, 0x3c); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_SENS); bit_set(0x1008, LED_SENS); while(1){ sel = select_string(menu_principal, 2); config = 1; if(sel==0){ bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_SENS); sel = select_string(menu_seguir_luz, 2); if(sel==0){ segue_luz_vertical(); } else if(sel==1){ segue_luz_horizontal(); } } else if(sel==1){ while(config){ sel = select_string(menu_seguir_linha, 6); //vermelho, verde, azul, amarelo, preto; switch(sel){ case 0: sel = select_string(menu_acao_cor, 4); vermelho = sel; if (sel == 2){ while(!start_button()){ tempoEmp=knob_int_value(1,10); printf("Tempo empurrar = %d segundos\n",tempoEmp); msleep(100L); } push_red = tempoEmp; } break; case 1: sel = select_string(menu_acao_cor, 4); verde = sel; if (sel == 2){ while(!start_button()){ tempoEmp=knob_int_value(1,10); printf("Tempo empurrar = %d segundos\n",tempoEmp); msleep(100L); } push_green = tempoEmp; } break; case 2: sel = select_string(menu_acao_cor, 4); azul = sel; if (sel == 2){ while(!start_button()){ tempoEmp=knob_int_value(1,10); printf("Tempo empurrar = %d segundos\n",tempoEmp); msleep(100L); } push_blue = tempoEmp; } break; case 3: sel = select_string(menu_acao_cor, 4); amarelo = sel; if (sel == 2){ while(!start_button()){ tempoEmp=knob_int_value(1,10); printf("Tempo empurrar = %d segundos\n",tempoEmp); msleep(100L); } push_yellow = tempoEmp; } break; case 4: sel = select_string(menu_acao_cor, 4); preto = sel; if (sel == 2){ while(!start_button()){ tempoEmp=knob_int_value(1,10); printf("Tempo empurrar = %d segundos\n",tempoEmp); msleep(100L); } push_black = tempoEmp; } break; case 5: segue_linha(); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_SENS); bit_set(0x1008, LED_SENS); msleep(500L); config = 0; break; } } } } printf("I See You! Good Night!\n"); } void empurrar(int seg){ int count=0; motor(MOTOR_R, 80); motor(MOTOR_L, 80); while(count<seg){ msleep(1000L); count++; } motor(MOTOR_R, 0); motor(MOTOR_L, 0); } void direita(){ int rodou1=0; int rodou3=0; int furos = 4; int speed = 90; int VMOTOR_1 = speed; int VMOTOR_3 = -speed; encoder0_counts=0; encoder4_counts=0; while(rodou1<170 ){ motor(1,VMOTOR_1); motor(3,VMOTOR_3); printf("0: %d ", rodou1); printf("1: %d\n", rodou3); rodou1 += encoder4_counts; rodou3 += encoder0_counts; if (encoder4_counts < furos){ VMOTOR_1 += 15; } else if (encoder4_counts > furos){ VMOTOR_1 -= 15; } if (encoder0_counts < furos){ VMOTOR_3 -= 15; } else if (encoder0_counts > furos){ VMOTOR_3 += 15; } encoder0_counts = 0; encoder4_counts = 0; msleep(50L); } off(0); off(1); } void esquerda(){ int rodou1=0; int rodou3=0; int furos = 4; int speed = 90; int VMOTOR_1 = -speed; int VMOTOR_3 = speed; encoder0_counts=0; encoder4_counts=0; while(rodou1<170 ){ motor(1,VMOTOR_1); motor(3,VMOTOR_3); printf("0: %d ", rodou1); printf("1: %d\n", rodou3); rodou1 += encoder4_counts; rodou3 += encoder0_counts; if (encoder0_counts < furos){ VMOTOR_1 += 15; } else if (encoder0_counts > furos){ VMOTOR_1 -= 15; } if (encoder4_counts < furos){ VMOTOR_3 -= 15; } else if (encoder4_counts > furos){ VMOTOR_3 += 15; } encoder0_counts = 0; encoder4_counts = 0; msleep(50L); } off(0); off(1); } void re(){ motor(MOTOR_R, -80); motor(MOTOR_L, -80); msleep(1500L); off(0); off(4); } int detecta_cor(){ int i, red, green, blue; int color_limit[5][3][2]; color_limit[RED][RED][0]= 135; color_limit[RED][RED][1]= 203; color_limit[RED][GREEN][0]= 199; color_limit[RED][GREEN][1]= 240; color_limit[RED][BLUE][0]= 165; color_limit[RED][BLUE][1]= 235; color_limit[GREEN][RED][0]= 195; color_limit[GREEN][RED][1]= 235; color_limit[GREEN][GREEN][0]= 118; color_limit[GREEN][GREEN][1]= 189; color_limit[GREEN][BLUE][0]= 155; color_limit[GREEN][BLUE][1]= 215; color_limit[BLUE][RED][0]= 220; color_limit[BLUE][RED][1]= 255; color_limit[BLUE][GREEN][0]= 185; color_limit[BLUE][GREEN][1]= 220; color_limit[BLUE][BLUE][0]= 95; color_limit[BLUE][BLUE][1]= 185; color_limit[YELLOW][RED][0]= 120; color_limit[YELLOW][RED][1]= 170; color_limit[YELLOW][GREEN][0]= 120; color_limit[YELLOW][GREEN][1]= 184; color_limit[YELLOW][BLUE][0]= 145; color_limit[YELLOW][BLUE][1]= 215; color_limit[BLACK][RED][0]= 204; color_limit[BLACK][RED][1]= 250; color_limit[BLACK][GREEN][0]= 190; color_limit[BLACK][GREEN][1]= 228; color_limit[BLACK][BLUE][0]= 185; color_limit[BLACK][BLUE][1]= 215; analog(SENS_COL); i = 0; bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); msleep(500L); bit_set(0x1008, LED_R); red = 0; while(i < 50){ red += analog(SENS_COL); msleep(100L); i++; } i = 0; bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); msleep(500L); bit_set(0x1008, LED_G); green = 0; while(i < 50){ green += analog(SENS_COL); msleep(100L); i++; } i = 0; bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); msleep(500L); bit_set(0x1008, LED_B); blue = 0; while(i < 50){ blue += analog(SENS_COL); msleep(100L); i++; } red = red/50; green = green/50; blue = blue/50; printf("\n"); printf("r:%d g:%d b:%d", red, green, blue); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); if(color_limit[RED][RED][0] < red && color_limit[RED][RED][1] > red && color_limit[RED][GREEN][0] < green && color_limit[RED][GREEN][1] > green && color_limit[RED][BLUE][0] < blue && color_limit[RED][BLUE][1] > blue){ printf("red\n"); return RED; }else if(color_limit[GREEN][RED][0] < red && color_limit[GREEN][RED][1] > red && color_limit[GREEN][GREEN][0] < green && color_limit[GREEN][GREEN][1] > green && color_limit[GREEN][BLUE][0] < blue && color_limit[GREEN][BLUE][1] > blue){ printf("green\n"); return GREEN; }else if(color_limit[BLUE][RED][0] < red && color_limit[BLUE][RED][1] > red && color_limit[BLUE][GREEN][0] < green && color_limit[BLUE][GREEN][1] > green && color_limit[BLUE][BLUE][0] < blue && color_limit[BLUE][BLUE][1] > blue){ printf("blue\n"); return BLUE; }else if(color_limit[YELLOW][RED][0] < red && color_limit[YELLOW][RED][1] > red && color_limit[YELLOW][GREEN][0] < green && color_limit[YELLOW][GREEN][1] > green && color_limit[YELLOW][BLUE][0] < blue && color_limit[YELLOW][BLUE][1] > blue){ printf("yellow\n"); return YELLOW; }else if(color_limit[BLACK][RED][0] < red && color_limit[BLACK][RED][1] > red && color_limit[BLACK][GREEN][0] < green && color_limit[BLACK][GREEN][1] > green && color_limit[BLACK][BLUE][0] < blue && color_limit[BLACK][BLUE][1] > blue){ printf("black\n"); return BLACK; }else{ printf("fuuuu\n"); return -1; } return 0; } int procura_luz(){ int min, value, count; motor(MOTOR_R, -20); motor(MOTOR_L, 20); while(count < 100){ value = analog(SENS_DIF); if(min > value){ min = value; } msleep(100L); count++; } return min; } void andaReto(int dist){ int inv3 = 0; int inv1 = 0; int rodou3 = 0; int rodou1 = 0; int furos = 6; int speed = 66; int VMOTOR_1 = speed; int VMOTOR_3 = speed; encoder0_counts = 0; encoder4_counts = 0; if (inv3) VMOTOR_3 = -speed; if (inv1) VMOTOR_1 = -speed; while(rodou3<dist){ rodou3 += encoder0_counts; rodou1 += encoder4_counts; if (encoder0_counts < furos){ if(inv3) VMOTOR_3 -= 4; else VMOTOR_3 += 4; } else if (encoder0_counts > furos){ if(inv3)VMOTOR_3 += 4; else VMOTOR_3 -= 4; } if (encoder4_counts < furos){ if(inv1) VMOTOR_1 -= 4; else VMOTOR_1 += 4; } else if (encoder4_counts > furos){ if(inv1)VMOTOR_1 += 4; else VMOTOR_1 -= 4; } encoder0_counts = 0; encoder4_counts = 0; motor(3,VMOTOR_3); motor(1,VMOTOR_1); printf("3: %d ", VMOTOR_3); printf("1: %d\n", VMOTOR_1); msleep(50L); } off(3); off(1); } void segue_luz_vertical(){ int light, polarizada, min=1000, value,valuec, count; motor(MOTOR_R, -20); motor(MOTOR_L, 20); count = 0; while(count < 500){ value = analog(SENS_DIF); valuec = analog(SENS_CDR); if(min > value+valuec){ min = value+valuec; } msleep(50L); count++; printf("%d %d\n",min,count); } printf("saiiiii\n"); count = 0; min = min + 10; while(1){ value=analog(SENS_DIF); valuec=analog(SENS_CDR); printf("%d %d\n",min,value); if( value+valuec< min){ andaReto(10000); break; } msleep(50L); } while(1){ msleep(10000L); } return; } void segue_luz_horizontal(){ int light, polarizada, min=0, value, valuec, count; motor(MOTOR_R, -20); motor(MOTOR_L, 20); count = 0; while(count < 500){ value = analog(SENS_DIF); valuec = analog(SENS_CDR); if(min < 1000 + value - valuec){ min = 1000 + value - valuec; } msleep(50L); count++; printf("%d %d\n",min,count); } printf("saiiiii\n"); count = 0; min = min - 10; while(1){ value=analog(SENS_DIF); valuec = analog(SENS_CDR); printf("%d %d\n",min,value); if(1000 + value - valuec > min){ andaReto(10000); break; } msleep(50L); } while(1){ msleep(10000L); } return; } void segue_linha(){ int rodou0, rodou1, VMOTOR_0, VMOTOR_1, furos, speed, i, slow, threshold, newOptB; int antOptL, antOptR, antOptB; int newOptL, newOptR; int state, fora, dentro,cor=0,acao=0; antOptL = digital(SENS_OPT_L); antOptR = digital(SENS_OPT_R); antOptB = digital(SENS_OPT_B); furos = 45; speed = 80; slow = 0; threshold = 80; state = 0; fora = 1; dentro = 0; bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_SENS); bit_set(0x1008, LED_SENS); while(1){ newOptL = digital(SENS_OPT_L); newOptR = digital(SENS_OPT_R); //newOptB = digital(SENS_OPT_B); if(digital(SENS_BRE) == 0){ motor(MOTOR_R ,0); motor(MOTOR_L ,0); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_SENS); cor=detecta_cor(); while(cor==-1){ cor=detecta_cor(); } if(cor==RED)acao=vermelho; if(cor==GREEN)acao=verde; if(cor==BLUE)acao=azul; if(cor==YELLOW)acao=amarelo; if(cor==BLACK)acao=preto; msleep(1000L); switch(acao){ //direita case 0: re(); direita(); motor(MOTOR_L, 20); motor(MOTOR_R, 100); state=3; antOptL = fora; antOptR = fora; break; //esquerda case 1: re(); esquerda(); motor(MOTOR_L, 100); motor(MOTOR_R, 20); state=3; antOptL = fora; antOptR = fora; break; //empurrar case 2: switch(cor){ case RED: empurrar(push_red); break; case BLUE: empurrar(push_blue); break; case GREEN: empurrar(push_green); break; case YELLOW: empurrar(push_yellow); break; case BLACK: empurrar(push_black); break; } break; //parar case 3: break; } if(acao!=0 && acao!=1) break; } bit_clear(0x1008, LED_R); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_G); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_B); bit_clear(0x1008, LED_SENS); bit_set(0x1008, LED_SENS); msleep(100L); if (antOptL == dentro && antOptR == dentro){ if (newOptL == fora && newOptR == dentro /*&&(newOptB == dentro || (antOptB == fora && newOptB == fora))*/){ state = 2; printf("direita | %d | %d \n", newOptL, newOptR); } else if (newOptL == dentro && newOptR == fora /*&& (newOptB == dentro || (antOptB == fora && newOptB == fora))*/){ state = 1; printf("esquerda | %d | %d \n", newOptL, newOptR); } else if (newOptL == dentro && newOptR == dentro){ state = 0; printf("adiante | %d | %d \n", newOptL, newOptR); } } else if(antOptL == dentro && antOptR == fora){ if (newOptL == fora && newOptR == fora){ state=1; } }else if(antOptL == fora && antOptR == dentro){ if (newOptL == fora && newOptR == fora){ state=2; } }else printf("ignorar | %d | %d \n", newOptL, newOptR); switch(state){ case 0: //continua reto encoder0_counts = 0; encoder4_counts = 0; VMOTOR_0 = speed; VMOTOR_1 = speed; if (encoder0_counts < furos){ VMOTOR_0 += 4; } else if (encoder0_counts > furos){ VMOTOR_0 -= 4; } if (encoder4_counts < furos){ VMOTOR_1 += 4; } else if (encoder4_counts > furos){ VMOTOR_1 -= 4; } encoder0_counts = 0; encoder4_counts = 0; motor(MOTOR_R ,VMOTOR_0); motor(MOTOR_L ,VMOTOR_1); msleep(50L); case 1: //desvia para esquerda motor(MOTOR_L, slow); motor(MOTOR_R, speed); msleep(50L); break; case 2: //desvia para direita motor(MOTOR_L, speed); motor(MOTOR_R, slow); msleep(50L); break; case 3: break; } antOptL = newOptL; antOptR = newOptR; } } /****************************** hbmenu.c ********************************/ /* Menu functions which also allow variables to be set via the knob and selection buttons Version 1.0 Written for MIT 6.270 contest by Anne Wright 11/14/1991 Version 2.0 Converted for Handy Board for Botball by Anne Wright 1/13/2001 */ /* abstractions for chosen_button */ #define NEITHER_B 0 #define START_B 1 #define STOP_B 2 /* abstractions for wait_button */ #define UP_B 3 #define DOWN_B 4 #define CYCLE_B 5 /*****************************button routines*************************/ /* Return minimum of two integers */ /* defined in cmucam3.ic which is loaded by this file -dpm 1/03 int min(int a,int b) { if(a<b) return(a); else return(b); } */ /* Return minimum of two floats */ float fmin(float a,float b) { if(a<b) return(a); else return(b); } /* Returns which button is depressed using definitions above. If both are pressed, start has precedence */ int chosen_button() { if(start_button()) return START_B; else if(stop_button()) return STOP_B; else return NEITHER_B; } /* wait until button is depressed(DOWN_B), released(UP_B), or both(CYCLE_B) and return which button if any activated the sequence */ int wait_button(int i) { if(i==DOWN_B){ while(!(start_button() || stop_button())); return chosen_button(); } else if (i==UP_B) { int b; b=chosen_button(); while(start_button() || stop_button()); return b; } else { int b; while(!(start_button() || stop_button())); b=chosen_button(); while(start_button() || stop_button()); return b; } } /********************* Knob to Number routines*****************************/ /* Returns an integer value from min_val to max_val based on the current position of the knob */ int knob_int_value(int min_val,int max_val) { int val, coarseness=(255)/(max_val-min_val),selection; val=min((knob())/coarseness+min_val,max_val); return min(val,max_val); } /* Returns an float value from min_val to max_val based on the current position of the knob */ float knob_float_value(float min_val,float max_val) { float val, coarseness=(255.)/(max_val-min_val),selection; val=fmin(((float)knob())/coarseness+min_val,max_val); return fmin(val,max_val); } /******************** Menu selection routines ****************************/ /* While waiting for a button press, display the string passed in and the val, the integer value betwen min_val and max_val for the knob. If the button pressed is the start button, returns the final value of val. If the button pressed is the stop button, returns -1. */ int select_int_value(char s[],int min_val,int max_val) { int val, button; printf("%s %d to %d\n",s,min_val, max_val); sleep(0.8); /* Wait until no button is pressed */ wait_button(UP_B); /* While no button is pressed, display the string passed in and the current value of val */ while((button = chosen_button())==NEITHER_B) { val=knob_int_value(min_val,max_val); printf("%s %d\n",s,val); msleep(100L); } /* Wait until no button is pressed */ wait_button(UP_B); if(button==STOP_B) return(-1); /** -1 means stop pressed -- do not reset value **/ else return(val); /* Stop not pressed, return val */ } /* While waiting for a button press, display the string passed in and the val, the float value betwen min_val and max_val for the knob. If the button pressed is the start button, returns the final value of val. If the button pressed is the stop button, returns -1. */ float select_float_value(char s[],float min_val,float max_val) { float val; int button; printf("%s %f to %f\n",s,min_val, max_val); sleep(0.8); /* Wait until no button is pressed */ wait_button(UP_B); /* While no button is pressed, display the string passed in and the current value of val */ while((button = chosen_button())==NEITHER_B) { val=knob_float_value(min_val,max_val); printf("%s %f\n",s,val); msleep(100L); } /* Wait until no button is pressed */ wait_button(UP_B); if(button==STOP_B) return(-1.0); /** -1 means stop pressed -- do not reset value **/ else return(val); /* Stop not pressed, return val */ } /* While waiting for a button press, display the string from the array of strings passed in which corresponds to the current position of the knob (see select_int_value). If the button pressed is the start button, returns the index of the string selected (0 to n-1). If the button pressed is the stop button, returns -1. */ int select_string(char choices[][],int n) { int selection,last_selection=-1,button; if(n>_array_size(choices)) n=_array_size(choices); /* Wait until no button is pressed */ wait_button(UP_B); /* While no button is pressed, display the string from the array of strings passed in which corresponds to the current position of the knob */ while((button = chosen_button())==NEITHER_B) { selection=knob_int_value(0,n-1); if(selection!=last_selection) { printf("%s\n",choices[selection]); msleep(150L); last_selection=selection; } } /* Wait until no button is pressed */ wait_button(UP_B); if(button==STOP_B) return(-1); /** -1 means stop pressed -- do not reset value **/ else return(selection); /* Stop not pressed, return val */ } /* * Local variables: * comment-column: 40 * c-indent-level: 4 * c-basic-offset: 4 * End: */
Conclusão
Neste trabalho, modificamos o robô anteriormente construído para adequá-lo à realização de novas tarefas: seguir uma fonte de luz polarizada, se deslocar sobre uma linha preta previamente traçada, interagir de diferentes maneiras com blocos de várias cores. Utilizamos sensores como o opto-reflexivo, o diferencial e o break beam para fazer as detecções necessárias de maneira satisfatória, sendo que as maiores dificuldades foram encontradas em torno da má precisão dos sensores utilizados. Os objetivos do trabalho foram atingidos, sendo o trabalho então concluído com sucesso.
Referências
MARTIN, Fred G. Interactive C User's Guide MIT Media Laboratory. Manual Edition 0.9. 1997.
MARTIN, Fred G. Robotic Explorations: An Introduction to Engineering Through Design. Prentice Hall; ISBN: 0-130-89568-7.
MARTIN, Fred G. The Handy Board Technical Reference. at
http://handyboard.com/oldhb/techdocs/hbmanual.pdf
MARTIN, Fred G. The Art of LEGO Design. Journal for Robot Builders,
volume 1, number 2. March 15, 1995
